If You Don’t Like Dogs, Does That Make You A Neanderthal?
We dog lovers are feeling a bit superior over a hot new theory indicating that wolf-dogs allowed modern humans to beat out our caveman rivals.
By Vicki Croke
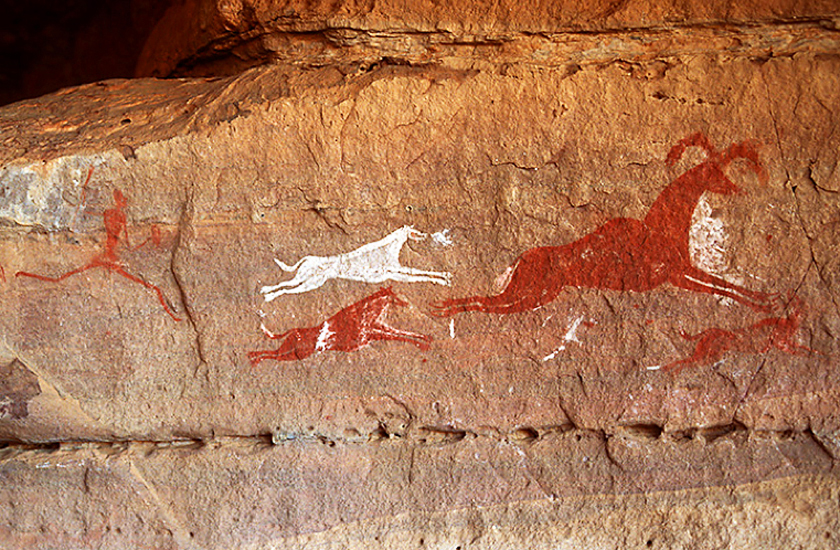
Rock art depicting man hunting with dogs. Tadrart Acacus, Libya. Photo courtesy of Peter Boekamp and the Bradshaw Foundation.
Is it possible that along with being happier and healthier, we dog lovers are also more evolved than those who don’t like dogs? Probably not, but for fun, lets use some emerging science to make the case.
First of all, new fossil discoveries, genetic data, and a hot new book by anthropologist Pat Shipman are giving real lift to the idea that modern humans outcompeted Neanderthals in part because we had wolf/dogs and they didn’t. That alone would make us dog lovers gleeful, but then, there’s a possibility that we could be downright smug. Because if you add in the fact that most of us humans today have anywhere from one to four percent of Neanderthal genes in our systems, depending on the individual, you might just wonder if dog loving might be an indicator of the ratio of Neanderthal genes you’ve got.
The second part is pretty sketchy, actually, but I liked it when I first heard of it three years ago, while reviewing the book “The $60,000 Dog,†by Lauren Slater. She wrote, with some humor, that theories about Neanderthals and dogs might tell us something about the people around us today: “What this may mean: all those ‘not dog’ people, the ones who push away the paws and straighten their skirts after being sniffed, well, they may have one foot in the chromosomally compromised Neanderthal pool.†We dog lovers, she asked? “Well, we may be displaying not idiocy or short-sighted sentimentality, as our critics would call it, but a sign of our superior genetic lineage.â€
Those words have really come back to me this month as Pat Shipman’s new book–“The Invaders: How Humans And Their Dogs Drove Neanderthals to Extinction†–is getting a lot of buzz. She makes a very persuasive and full case that early dogs were critical to modern humans beating out Neanderthals in the game of life.
According to The Atlantic:
One of the most compelling — and enduring — mysteries in archaeology concerns the rise of early humans and the decline of Neanderthals. For about 250,000 years, Neanderthals lived and evolved, quite successfully, in the area that is now Europe. Somewhere between 45,000 and 35,000 years ago, early humans came along.
They proliferated in their new environment, their population increasing tenfold in the 10,000 years after they arrived; Neanderthals declined and finally died away.
But, according to The Guardian, the question is: what killed off those Neanderthals?:
Some scientists blame climate change. Most argue that modern humans – armed with superior skills and weapons – were responsible. Shipman agrees with the latter scenario, but adds a twist. We had an accomplice: the wolf.
Modern humans formed an alliance with wolves soon after we entered Europe, argues Shipman. We tamed some and the dogs we bred from them were then used to chase prey and to drive off rival carnivores, including lions and leopards, that tried to steal the meat.
The timing of the human-dog bond is critical to this theory. We used to think that wolves were domesticated only about 10,000 or 15,000 years ago, and that would mean dogs weren’t around for the great modern human vs. Neanderthal competition. But new data is pushing back the timing of our first associations with early dogs.
We’ve got that evidence from biologists and archeologists now. For me, these little glimpses of our earliest associations with wolf dogs, told in fossils and ancient imprints, are always so evocative. For instance, from a cave in Southern France, there are footprints made in mud and preserved for thousands of years—one set those of a child walking along barefoot and right next to them, step for step, are the paw prints of a large dog or wolf. They date back 26,000 years.

Did the disappearance of Neanderthals go hand in hand with the growing bond between humans and wolf dogs? Photo: Bruce Funston/Wikimedia Commons.
There are other recent fossil discoveries from the Czech Republic, Siberia, and Belgium indicating a dog-wolf/human bond starting at least back 33,000 years ago. And some doggie DNA analysis says wolves could have started becoming dogs 135,000 years ago. Mark Derr has written eloquently about this ancient dog-human bond framed not as us taming them, but as an “alliance,†and an “evolutionary inevitability.â€
But even if there’s a good argument to be made that modern humans beat out Neanderthals because of a love of dogs, what about the notion that people who don’t like dogs have more Neanderthal in them? Well, as it turns out, our ancestors did have sex with Neanderthals, and parts of Neanderthal genetic code is alive and well in many people.
According to National Geographic’s “Genographic Projectâ€:
Everyone living outside of Africa today has a small amount of Neanderthal in them, carried as a living relic of these ancient encounters. A team of scientists comparing the full genomes of the two species concluded that most Europeans and Asians have between 1 to 4 percent Neanderthal DNA. Indigenous sub-Saharan Africans have no Neanderthal DNA because their ancestors did not migrate through Eurasia.
Intriguingly, “Levels of Neanderthal ancestry differ in European and Asian groups,†according to a study cited by Discovery News. “Han Chinese people in Beijing, for example, have the most such ancestry while Puerto Ricans have the least.â€
If that makes you wonder how high you score for Neanderthal ancestry, you’re not alone. An Associated Press story included a quote from New York University anthropology professor Todd Disotell, who says he did something about his curiosity. “Disotell recently had his genome tested by a private company and found he’s got more Neanderthal DNA than most people, about 2.9 percent: ‘I’m quite proud of that.’ ”
Here was my chance to test the theory at least with a sample of one. I emailed Professor Disotell to ask if he likes dogs. He responded: “I have a Golden retriever who I love.†Oops. So much for the theory that a higher amount of Neanderthal DNA makes people dislike dogs.


8 Responses to “If You Don’t Like Dogs, Does That Make You A Neanderthal?”
its known that neanderthals had big head and they were smart too…but how did they fail to use other animals for fighting purpose like early homo sapiens….
No one really knows if wandering Neanderthals had pets. Most likely they did like many surviving hunter gathers today.
I must have a lot of Neanderthal in me then, because I can’t stand dogs.
Really?
My son’s Labrador, Bailey, told me it is well known among dogs that Neanderthals were cat lovers, good riddance. She also revealed that dogs have uncovered a worldwide conspiracy among squirrels. This is why they must be chased.
3.8 percent Neanderthal. 4.1 percent Denisovan. 4 dogs own me currently.
I must be 6% Neanderthal, dogs bark at me front inside their houses when I walk by
I dislike being around dogs intensely, yet I according to 23 & me I have VERY FEW neanderthal variants.
Comments are closed.